What is RTT (Round-Trip Time)
Round trip time is measured in milliseconds. It is the total time taken by a user’s request to reach the server and return to the user. The lower the round tip time, the higher the efficiency of a network.In this article today, we will discuss everything that you need to learn about Round Trip Time.
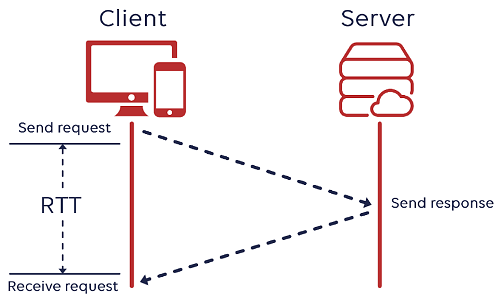
How to Measure Round Trip Time
You can estimate the RTT with ping. It’s the most common tool.
Here’s the definition of a ping:
A ping is a command-line tool that bounces a request of a server and calculates the time taken to reach a user device.
In case of network congestion and server throttling due to higher traffic, the actual RTT would be more than the measured RTT.
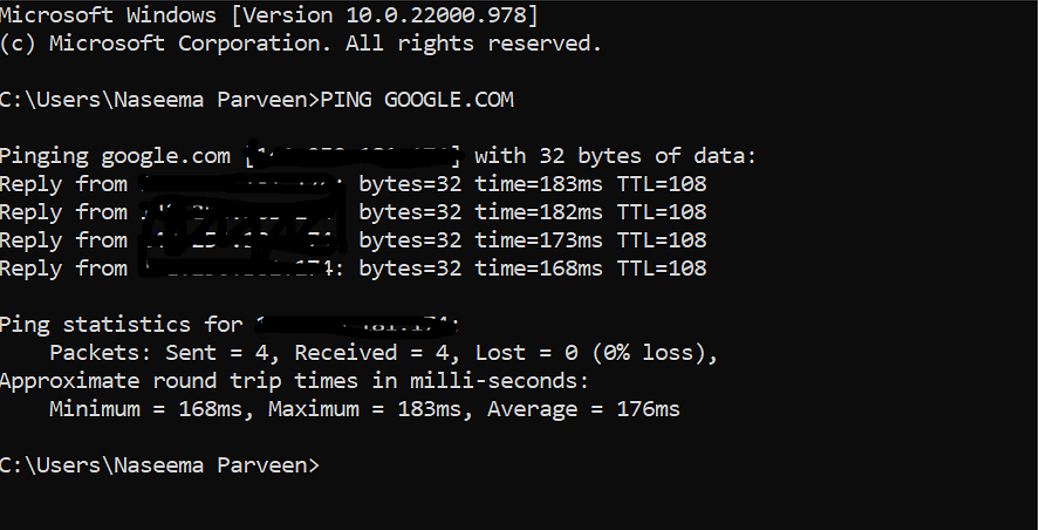
So, here are ping statistics for Google.com which is an average of 176 ms.
In order to calculate ping for your network, follow these steps:
- Open Windows Search Bar;
- Then type CMD into the search bar;
- Click Open;
- Type ping followed by a space and an IP address or domain name;
- Hit Enter on your keyboard;
- The ping test results will appear on your screen.
How does round-trip time work?
Round Trip time uses CDN to speed up the delivery of the information. Using CDN can company can ensure its round trip time is lesser which improves. As a result, the overall efficiency and speed of the content delivery process improve.
Let’s suppose a company has a main server in Canada, and if a user in India tries to access the data, the network will first receive the query, send it to the server in Canada, and returns it to India. The time taken for the data to travel from the source to destination, and then return to the source is called RTT which is the time taken by data to have a complete round trip. It is measured in milliseconds.
CDN for RTT
In the above example, the RTT would be higher because the request has to travel through the network to another country. CDN is used to avoid this so that the request is served from the locality. CDN is a network of geographically distributed data centers that allow the user to receive information within a short period, thus reducing RTT.
Bonus tip:
Remember RTT can not be measured accurately, and it’s an estimated time, not an accurate time.
Factors Influencing RTT
Several factors influence RTT including the physical distance, network traffic, the infrastructure of the components, and network congestion. They affect the overall transit time.
Let’s get into the detail of each factor influencing RTT.
Server response time
The server response time plays a critical role in determining the RTT. During the times like DDoS attacks, the server is sluggish and it can not actively respond to any queries that it receives, which makes it hard to return the data quickly. The server does not process your request instantly and therefore the RTT is higher.
Traffic levels
Higher traffic levels and traffic surge directly increase the RTT. This happens particularly during a live show, or matches. Since the servers and data centers have to cope with the instant traffic, it takes time to process it and therefore the round trip time increases drastically.
During the times when traffic is high, there is network congestion and server throttling, and thus the RTT is higher.
LAN Traffic
Your local area network traffic highly affects the RTT. Sometimes the local area network acts as a bottleneck for your network. Even before the requests reach the larger internet, if a large number of people are streaming video in a particular locality, the RTT may increase even when the main server can process the request.
Number of network hops
The higher the network hops and node counts, the higher the will be RTT. A node count is an intermediate server that takes time to process the user query and responds to it. Depending on its path a connection will have to pass through a various number of nodes. The greater the nodes the slower the will be a connection, and thus it increases RTT.
Therefore it’s great to reduce the number of nodes to reduce the RTT.
Transmission medium
Different mediums are used for transmitting a signal. Some transmission mediums include copper, fiber optics, wireless frequency, satellite communication, etc. How fast your connection is based on the nature of your transmission medium.
A network that is made over optical fiber will be efficient as compared to one made over copper. Thus, your RTT increases or decreases based on what medium your network has.
Distance
Distance is the total physical length a signal takes from the source (a user’s system) to reach the destination(server). The higher the distance between a server and end user, the more will be RTT.
CDN contributes significantly to reducing RTT and solving issues related to distance with the help of an edge server so that the query responds from the nearest edge server rather than traveling to the main server. You can try our service which can help to reduce RTT.
How to Reduce RRT
There are several ways to reduce RTT, some general tips would be:
- Removing the broken links ;
- Add files and stylesheets;
- Caching your browser ;
- Minimize the HTTPS redirects.
Let’s look into the other strategies that can help you reduce RTT at large.
Points of Presence (PoPs)
The dispersed PoPs which are the data centers are responsible for storing and caching data to deliver it to visitors in its vicinity. A signal has to travel less distance if there are more PoPs.
Web Caching
Web caching in CDN helps the user to get a response from the neared edge server rather than the main server, thus reducing the RTT. It also minimizes network congestion during the traffic surge. As a result, it improves the response time and minimizes RTT.
You can also cache data in your browsers locally to minimize the round trip time.
Scalability
The scalable feature of CDN allows the network to reduce the RTT. Since CDN operates in the cloud, it can process a huge number of requests, thus improving response time and decreasing congestion.
You can install an edge server closer to your users, and store relevant data on it. Every time a user requests content, it will be served from the nearest edge server rather than the main server in another country.
Load distribution
The RTT minimizes due to the reduction of load distribution by CDN. The edge servers in each geography respond to the requests during high traffic times, thus speeding up the server and reducing the RTT.
Conclusion
CDN improves the RTT by optimizing the routers between the locations and reducing latency. Make sure you incorporate CDN for better data placement, optimization, reducing latency & file size, and improving the RTT.



