The demand for live streaming and online video content is at its peak, especially in recent years, where working from home has become a need rather than an option. From video conferences to home security cameras, live streaming makes digital presence much easier. You can share your content with millions of viewers with just a few clicks and taps.
According to a report, most people spend about 16 hours a week watching videos (a 52% increase from the previous two years).
What is Live Streaming?
Streaming is the method used for continuous data transmission from a remote storage location to the client. This data is usually in audio or video format. The content is transmitted a few seconds at a time, allowing playback to start while the remaining content is still transferring. There is no need to download the content first.
Live streaming involves the continuous flow of the content in real-time. This content is not pre-recorded or stored anywhere. The audience receives data at the same moment as it is created.
What will you learn?
We hope to introduce you to the basics of Live Streaming and different protocols like HTTP(HLS), LL-HLS, and MPEG-DASH, their benefits, and drawbacks. This article will also help you understand the basics of a CDN and its uses for live streaming. You will also know about choosing the best CDN for live streaming. Let’s continue to learn more.
Why CDNvideo
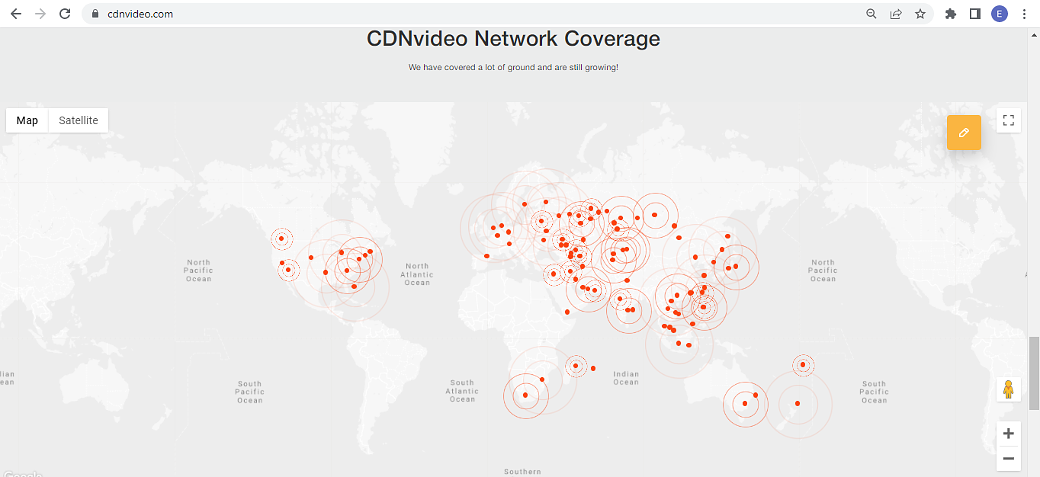
CDNvideo is one of the leading Content Delivery Network providers with headquarters in China. With 80,000 servers on five continents, live streaming is one of our core competencies. We have a network uptime of 99%, which assures uninterrupted services. Our servers can handle millions of users at a time, and we make sure your streams reach the country of your choice and are compatible with any device. Our live streaming services include:
- Content Transcoding;
- Live stream recording;
- Storage for the live stream;
- Digital Video Recording (DVR) option;
- Restream;
- Signal Reception from the Satellite.
All these services combined with the technical support of our professional staff, and state of art network, ensures a high-quality stream with the best possible speed. We have also developed unlimited cloud storage and an HTML 5 player that enables P2P streaming and 360-degree video demonstration. Unlike other platforms, CDNvideo’s content delivery (CDN) network supports the following methods of stream publication:
- RTMP-publish;
- RTMP-pull;
- RTSP-publish;
- RTSP-pull;
- MPEG_TS-publish;
- HTTP-pull.
You can also benefit from our auto-configuration self-service for RTMP/RTSP-publish to start on the go. We take pride in our live streaming services, and hundreds of customers have benefited from our services. Start your journey today by signing up, and enjoy the great live streaming services you were looking for.
How does CDNvideo’s Live Streaming work?
Here are the basics of CDNvideo’s live streaming.
- Capturing device (camera, microphone, etc.) captures the content.
- You have the option to send the audio/video stream to the local encoder for modification, or you can send the stream directly to CDNvideo through the internet.
- CDNvideo helps reduce the buffer by storing and distributing content from the nearest EDGE server to the viewers.
- CDNvideo then sends this data to a customized HTML5 video player.
Now let’s move on to a few important live-streaming protocols.
What is HTTP?
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is a protocol that transfers information between the devices in a network. Almost every website and application a user accesses runs on HTTP. Request and Response are key to the data transfer over the HTTP. In simple words, almost all HTTP messages are a request or a response to a request.
The request and response pattern is not applicable for HTTP streaming. While streaming, the client and server connection remains open for that specific duration. The server keeps sending the video data segments to the client, and there is no need for a request by the client.
This process will run smoothly with CDNvideo’s HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) encoder and its powerful video hosting platform. Now let’s move on to the technical aspects of the HLS and its working.
A media file is stored on the server for on-demand streaming. CDNvideo provides conversion from MP4 to HLS on the fly for the mp4 formats.
Our server runs 2 main processes: encoding and decoding.
- In encoding, the data format is changed into a recognizable format so that all the devices can easily access and interpret the data. An HLS must use H.264 or H.265 encoding.
- The next process is segmentation, where the video is divided into small segments of a few seconds in length. The default length of a segment is 6 seconds, but this may vary or change according to the specification of each customer by our Transcoding equipment.
HLS creates an index file to keep track of the order of the video segments. It also creates duplicate segments at different quality levels like 480p, 720p, 1080p, etc.
CDNvideo also provides transcoding services to combine different qualities into a single auto bitrate by crafting playlist m3u8.
The encoded video chunks are sent to the end user’s devices over the internet when the user requests a stream. A content delivery network (CDN) comes in handy in the distribution process, especially if the geographical area is wider and more diverse. CDN also helps in the quick delivery of the content by caching it.
The CDNvideo has a dedicated CDN that makes distribution much easier. Our CDN has no buffering and can handle unlimited users for a live stream. It is worth mentioning that we have handled more than one million viewers for a live stream of the FIFA world cup.
The end-user device plays the video after receiving the stream and decoding it. This device may be a smartphone, desktop, or any other device capable of playing a video. The end-user device uses the index file to play the video in order and can switch from a lower-quality picture to a higher quality as needed.
HLS is one of the most widely used and up-to-date protocols for media streaming. There are multiple benefits of the HLS:
- The HTTP live streaming is compatible with almost every device, browser, and firewall;
- HLS uses Adaptive Bitrate Streaming that enables the video player to switch between different video qualities depending on the network conditions;
- HLS uses TCP for transport which ensures no frames are missing in the delivery. This helps in smooth and distortion-free video playback;
- HLS has a greater potential for scalability, which helps better bandwidth management;
- It also helps reduce costs as you don’t have to worry about buying some dedicated devices for the stream;
- Supported on all devices;
- Larger buffer for storing chunks.
- Latency of 30-60 seconds.
- No Publishing from a browser.
What is LL-HLS?
One of the main drawbacks of the HLS is the higher latency. In 2020 Apple extended HLS, enabling it for lower latency, and introduced Low Latency HTTP Live Streaming (LL-HLS). The LL-HLS provides the same scalability as HLS but with a low latency of around 2 – 8 seconds. The basic working mechanism is the same as HLS. We will explain the main changes to the protocol.
- Each segment is further divided into mini-segments. These mini-segments disappear while the segments with the same date are available for a longer time.
- A playlist might contain ‘Preload Hints’ that allow a player to predict the data to be downloaded, which ultimately reduces the overhead.
- This update also provides an option for the servers to allocate unique identifiers to different versions of a playlist.
- One of the best features of the LL-HLS is the decreased latency, which improves the user experience and client credibility.
- It is compatible with a wide range of devices and browsers.
- This protocol has a decreased request rate from the user end, which reduces the incidence of request errors.
- It also aims to provide high-quality video content with no distortion.
- It provides seamless quality switching.
- LL-HLS is compatible with regular HLS, which is important for older browsers.
- The total delay from the camera to the viewer is from 2 to 4 seconds, depending on the device and settings.
Common errors that lead to the fact that the delay is not low, but the usual one, more than 10 seconds:
- the player is used without low latency mode. This happens when using third-party players. The CDNvideo player supports LL HLS by default. You can check the stream on our demo stand: https://players-stand.cdnvideo.ru/clappr/llhls/;
- Perhaps the URL is specified without HTTPS. In this case, HTTP 1.1 is used and low latency mode will not work (HTTP 2 is needed);
- Keyframes in the source stream should be exposed as often as possible;
- LL-HLS requires the newest IOS( IOS >=14).
What is MPEG-DASH?
MPEG-DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP) is another similar streaming protocol that runs over HTTP. Like HLS, MEPG-DASH works by breaking down the video into smaller segments. Users can choose the video quality according to their requirements as these segments encode at different quality levels.
This streaming method is also an international standard. CDNvideo’s MPEG-DASH streaming process works like this:
In the first step, a video file is divided into smaller chunks of a few seconds in length. Our origin server creates an index file. You have the option to use any encoding standard to encode these smaller chunks.
Our server pushes these smaller segments to the end user’s device over the internet. Our dedicated content delivery network helps in content distribution.
The end user’s device decodes the streamed data and plays the video in the final step. The video player automatically adjusts to the network conditions. It will show a high-quality picture for a strong network and switch to a low-quality for a low bandwidth network.
- MPEG-Dash is compatible with multiple devices, operating systems, and web browsers.
- It uses the fragmented MP4 (fMP4) format, designed specifically for streaming over the internet.
- MPEG-DASH is much more efficient than other delivery standards.
- The content quality is much higher with seamless switching.
- Higher Latency.
- Not compatible with the Apple devices.
Now that you know the basics of streaming protocols, let’s discuss CDN and its working and how you can use it for live streaming.
What is a CDN?
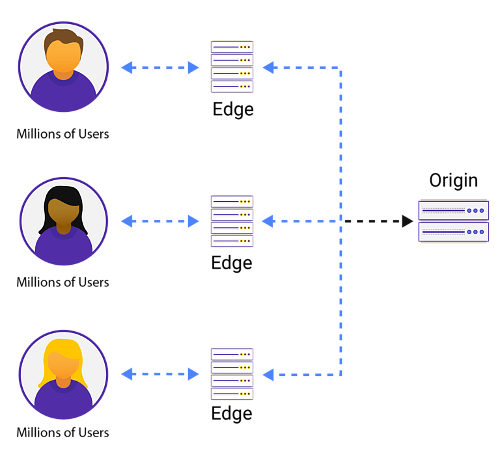
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a combination of multiple servers in different geographical locations.
These servers are linked to the origin server and have copies of the data stored in the origin server.
A CDN distributes this content based on the user’s location.
Why use a CDN for live streaming?
There are various benefits of using a CDN for live streaming. These benefits will add a positive user experience, and they will also help you retain your audience. According to Cisco, approximately 72 % of the internet traffic passes through a CDN.
The best thing about using a CDN for a live stream is that it is the fastest, most secure, and most reliable method to deliver content to multiple users in any part of the globe. CDNs are capable of handling large audiences.
CDN helps in reducing the load on servers. The request from the end user’s device goes to the CDN first, where it serves the request. The CDN cache will only forward that request to the origin server if the requested video segment is not present in the CDN’s cache.
The round trip time from a streaming location and a user is the key in a live stream. If your audience is far away from the live stream location and the time to play the video takes minutes, the user might abandon you and look for another service provider. CDN helps resolve this issue by serving the content from the nearest server location. It minimizes the request-response time and reduces download times and latency delays.
A buffer occurs when a streaming server has multiple requests at a time, and it cannot serve every player at a certain time. CDN also reduces buffering as the user requests do not travel back to the origin server.
A CDN is placed between the end-user and the live streaming server. Now think of it as an extra line of defense that protects the origin servers from DDoS attacks. Modern CDNs use sophisticated techniques of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI) and are well equipped to detect and block any malicious or harmful traffic or a Disturbed Denial of Service attack. These attacks will reach directly to the origin server in the absence of a CDN.
Salient features of CDNvideo’s Live Streaming CDN
Each CDN has its strengths and focuses on certain aspects. Some prefer a wider area coverage, while others opt for different types of content. From custom solutions to free trials, we provide CDN services that are best for your business needs. Following are a few strong features of our CDN.
We have a worldwide presence to ensure your content reaches the furthest corners of the globe. The number of servers determines the speed and scalability. More servers mean more bandwidth handling capacity.
The geographic distribution of the CDNvideo’s servers is another key feature. We provide live streaming services with a good server distribution rather than concentrated servers in a geographical location. CDNs operate through Points of Presence (PoP). These are the edge servers that transport the content directly to viewers. The end-user will experience good live streaming if he is close to a PoP edge server.
We have a ‘no-compromise’ policy on Quality and performance. We ensure the best solutions to speed, buffering problems, reliability, and latency.
Network security is another key feature that is vital for live streaming. Our CDN helps in minimizing DDoS attacks. We respect customer values and offer content protection and restricted content delivery to customers who are comfortable with a categorized audience.
The Pricing of CDNs depends on multiple factors like audience location, the geographic distribution of servers, content volume, etc. We have kept our prices flexible so that everyone could benefit from our services plus you can also enjoy volume discounts on different services. Apart from that, you can enjoy free 14-days free trial to make sure you are investing in the right place.
Conclusion
You cannot deny the fact that live streaming has seen exponential growth in recent years. It is hard to conclude which protocol is best as each protocol serves a different purpose and has its pros and cons. A protocol that provides the best streaming quality or a protocol that has a minimum delay, you have to choose what best suits you. Using a CDN for live streaming boosts your performance and reach, which results in good business. Choosing the best CDN through a credible platform is the key to overall performance.
CDNvideo has an edge over its competitors when it comes to CDN services. Be it broadcasting services or live game streaming, CDNvideo makes live streaming a piece of cake. There are over 600 companies that rely on CDNvideo’s services. It also offers competitive prices and volume discounts, maximum coverage with 86,000+ servers, and free HTTPS traffic with 99.99% uptime.