We all need a near-to-real-time experience whether we play video games, watch a NetFlix show, watch a game, or gamble. We think the live show we are watching is real-time, but the fact is takes a few milliseconds or seconds to reach us.
The gaming video, sports live, or concert that you are watching might not be live, but it might delay a few seconds, or so. It is because data travels from one place to another in chunks. Data travels at this speed (186,000 miles/sec). And, it might break or slow down to large extent, and that’s low latency is an important part of building a good user experience.
In this article today, we will explain what is latency, what is low latency, its importance, and some practical scenarios around how low latency is important in real-life cases.
What Is Latency?
According to Cloudflare
Network latency is the amount of time it takes for a data packet to go from one place to another.
Data travels from the server to the client’s device in bits, and the time taken for the data to reach the user is called latency. Low latency is important because delay in data transfer can create a poor user experience.
What Is Low Latency?
It is the lowest possible time taken for the data to reach your user. It aims to achieve the lowest possible delay. This is not a measurement of speed as such, but it aims to achieve the lowest possible delay.
Generally, a delay of 5 seconds or less is called low latency. In some cases, even a lower latency is required than 5 seconds, and that’s when ultra-low latency and near real-time streaming have emerged. An ultra-low latency might include one second or lesser. They are applicable where two-way chats and real-time device control are required.
Let’s first understand what causes latency
What Causes Latency
A low latency aims to receive data processing delays over a network. In general, the three major factors that cause latency include:
- Distance;
- Physical barriers;
- Congestion.
The raw data is first encoded. The process includes compressing and formatting files that need to be transferred over the network. The streaming server transcodes them, and they then go through CDN to various devices from where the video is streamed.
How Important Is Low Latency?
40% of viewers lose interest if the video doesn’t load quickly. Individuals and businesses require different levels of latency based on their needs. For example, if users are gambling or playing other video games they would look for the least latency. A delay of a single second could be troublesome for different individuals, and businesses.
Based on the needs, low latency is a business-critical consideration. The following graph shows the percentage of people who faced low latency.
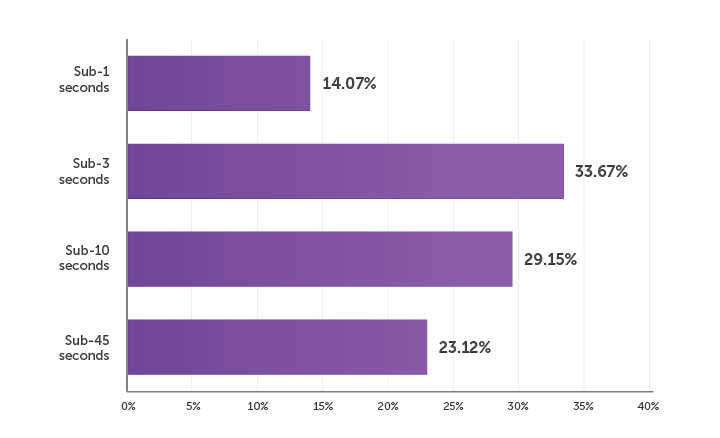
What Category of Latency Fits Your Scenario?
Various businesses have different streaming scenarios. For example, multiplayer online gaming and financial trading applications might need a different kind of latency.
You might to have work on your business needs to identify which one best fits for you:
- For video conferring & remote devices – You might need near real-time;
- Interactive content – Low latency;
- Live premium content – Reduced latency;
- linear programming and one-way streams – Typical HTTP Latencies.
4 Reasons Why Low Latency Is Becoming Vital – Case Studies
Low latency data transfer is a must for real-time business services, here’s how:
Nextgen Voice and Video Services
High-capacity, low-latency connections are required for streamlining the video and audio meetings including HD 4k/8k video quality for the clinical documentation to achieve their goal of healthier patients and happier providers. Whereas high latency causes poor voice quality, clipped speech, echo, and jitter resulting in poor client experiences.
Casino | gambling
The online gaming industry is exponentially expanding over the past years.
The goal of iGaming including casino, gambling is to give a great user experience to gamers. If the game loads too slowly, or in the worst cases it disconnects, or the video freezes, there’s no way your user will come back again to the streaming platform.
In other cases, the real-time data between the play, the supplier, and the operator might delay. It would be hard for you to handle financial transactions in real-time as well.
This could be possible due to factors related to latency. For example, a live dealer studio in Germany owns an online casino company and streams it in Libya, where the players are interacting from India and the rest of the world. The data will travel from Germany>Libya>Rest of the world.
To avoid this, the online casino company needs to integrate several systems, and leverage high-end technology to transfer data to/from players all across the world.

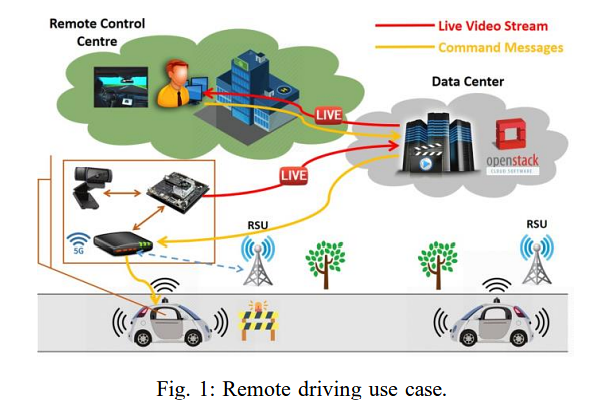
Autonomous Vehicles(IDK)
Autonomous vehicles will fail in absence of low latency. There is a myriad of data to be sent and received. The AV relies heavily on the internet of things because it requires a constant uplink to a whole lot of services in real-time. A huge amount of data needs to be transmitted throughout the process that includes GPS location, acceleration, engine status, battery status, and charging alter.
It also includes data on traffic congestion, weather alters, data from road sensors, etc. Since all this data needs to be sent and received in real time, AV strategy requires immediate sensor-based information and data-driven decision-making.
Along with the performance of the AV, it is also needed for the safety of the pedestrians on the road and the drivers of AV.
Virtual Reality and the Metaverse
The concept of virtual reality and metaverse is based on higher bandwidth and lower latency. The metaverse won’t work in case of a lack of network connectivity, and that’s where higher bandwidth and lower latency come into play.
Metaverse is highly dependent upon specialized hardware, powerful computers, and user-stored data that needs to be transmitted efficiently. Fast streaming technology and low latency make it possible to bring this into reality.
A high level of interaction and great user experience is everything in the metaverse. Real-time reaction and communication are only possible in case of low latency.
Who Needs Low Latency?
Low-latency streaming allows users to experience video streaming in real time. Minimizing the lag time is important in the following scenarios.
Low latency is needed in the following cases and is not limited to them:
- Second-Screen Experiences;
- Video Chat;
- Betting and Bidding;
- Video Game Streaming and Esports;
- Remote Operations;
- Real-Time Monitoring;
- Interactive Streaming and User-Generated Content.
Low-Latency Streaming Protocols
The best low-latency live streaming uses the HLS streaming protocol. It stands for HTTP Live Streaming. LL-HLS and FLV are the low-latency protocols. RTMP is used to push the video, but not for video streaming. RTMP is used to push the video which later can be converted to HLS, LL-HLS, FLV
LL-HLS Benefits
- One of the best features of the LL-HLS is the decreased latency, which improves the user experience and client credibility.
- It is compatible with a wide range of devices and browsers.
- This protocol has a decreased request rate from the user end, which reduces the incidence of request errors.
- It also aims to provide high-quality video content with no distortion.
- It provides seamless quality switching.
- LL-HLS is compatible with regular HLS, which is important for older browsers.
- The total delay from the camera to the viewer is from 2 to 4 seconds, depending on the device and settings.
FLV benefits
- Fast start: With FLV the streaming delay could be up to 2 seconds, and it is the fastest way to play any video on the web.
- Highest level of security: FLV provides a secure media delivery. It supports SSL encryption of streams.
- Video tracking, logging, and reporting: It gives you full control over statistics like, how long the video content has been viewed, how frequently the user navigated, etc.
- Offers advanced video control: FLV allows you to achieve quality of service monitoring, bandwidth detection, server-side playlists, and thumbnail creation on an autopilot basis.
- Minimal use of resources: FLV results in minimal use of resources. Since the client doesn’t own the whole file, it results in a reduction of memory and disk space .
How to Achieve Ultra-Low Latency
Here’s how you can achieve ultra-low latency
Have a flexible bandwidth and dedicated network speed
The interaction of the users with metaverse, casino, gambling, or AV cars is handled by the front-end web server. For efficient data delivery, and uninterrupted activity you need to have a high-speed network with better bandwidth.
Have a dedicated network that ensures seamless video transmission of the players
An uncapped bandwidth is what you need for your online video streaming. If you have a flexible bandwidth you won’t be capped during the large spikes of data.
Leverage Global CDN
If you adopt a CDN for your video streaming platform, here’s what it will do.
“CDN basically stores a replicated, or cached, version of website content in multiple points of presence (PoPs) all around the world, so that users can access it from the PoP that is located within the closest proximity to them”.
Servers & Infrastructure Geo-location that fulfills regular compliance
When you put your effort to achieve low latency, make sure you choose servers and infrastructure that should fulfill the regulatory compliance of the geography that you are streaming in.
Conclusion
For a better user experience, it’s important to choose a technology with low latency without compromising video quality. Choose a technology that has greater protocol compatibilities with unmatched speed and reliability.



